Seven Sisters Development Assistance
Livelihood Promotion
With whom do we work?
SeSTA’s Livelihood Promotion initiatives focus on empowering small and marginal farmers, landless households, and women through sustainable practices. For households with limited land, SeSTA promotes food security by increasing paddy productivity, growing pulses, and vegetables using System of Crop Intensification (SCI) techniques, and introducing animal husbandry like pig, goat, and poultry rearing. Landless households are supported through year-round animal rearing models, ensuring steady income. Agricultural techniques like System of Rice Intensification (SRI) and SCI for vegetables, coupled with backyard nutrition gardens, enhance food diversity and income. SeSTA also promotes farm ponds for fish farming and integrated farming on embankments.
Below mentioned are the SeSTA’s broad models:
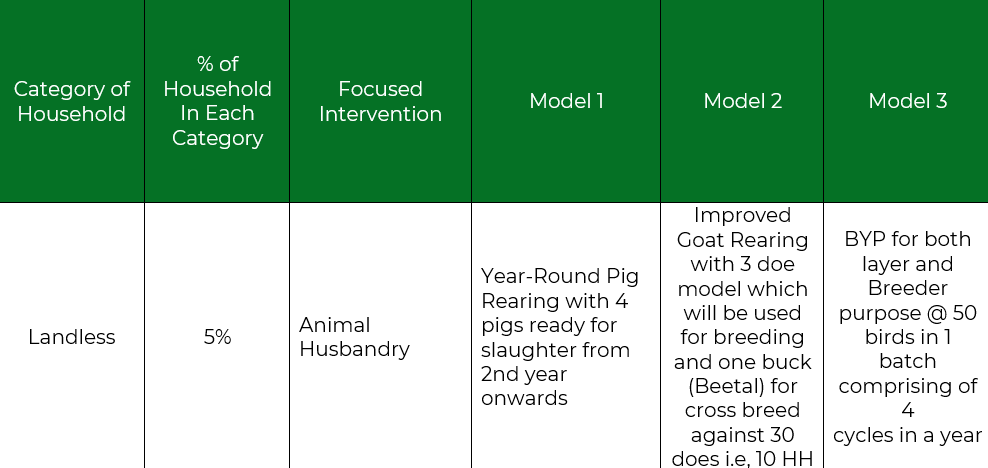
Landless Model
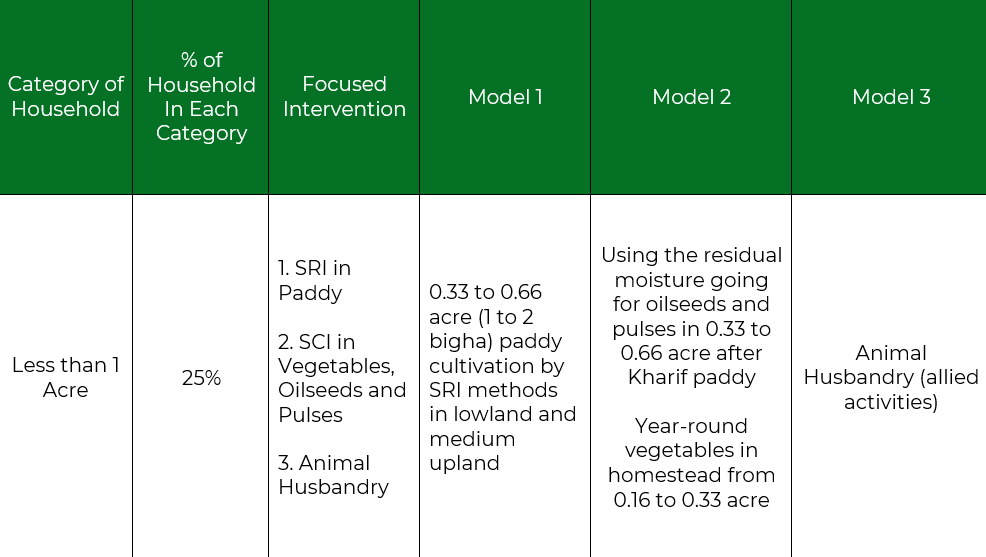
Less than 1 acre Model
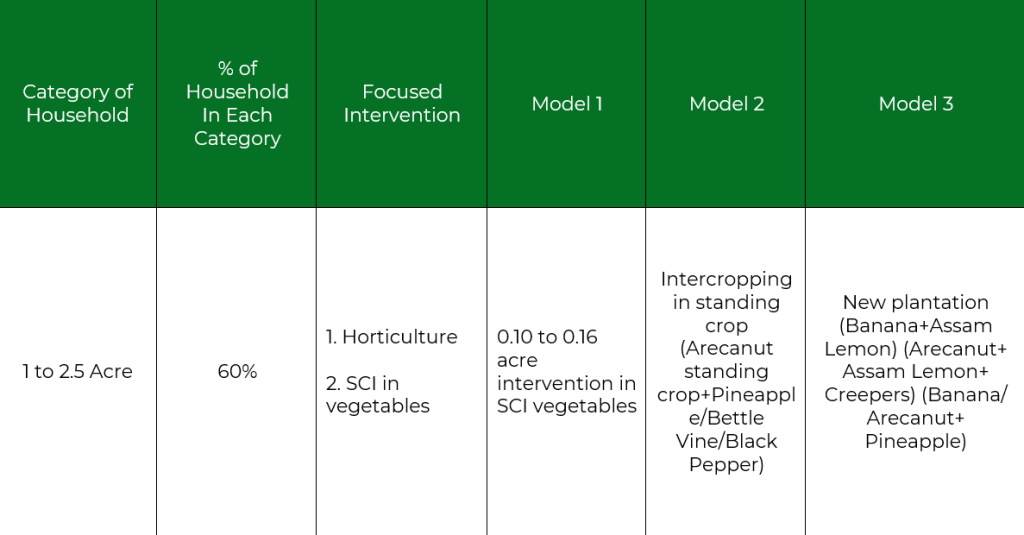
1 acre to 2.5 acres Model
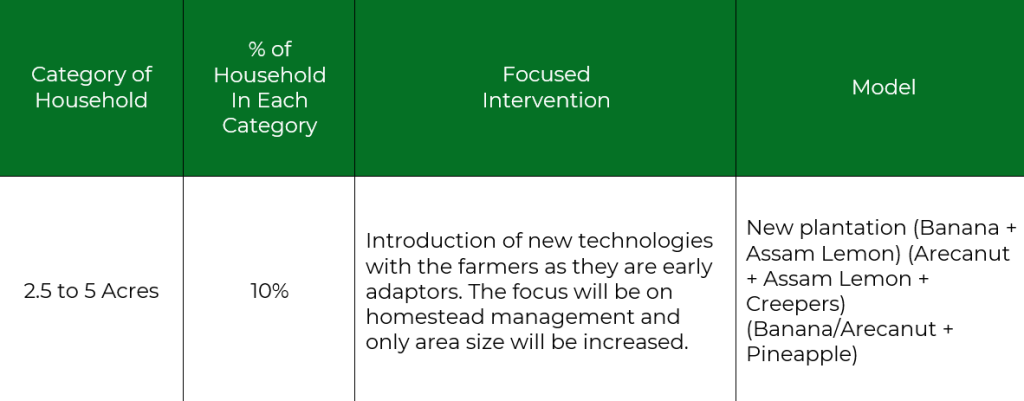
2.5 acres to 5 acres Model
Livelihood Interventions
SRI
The System of Rice Intensification involves cultivating rice with as much organic manure as possible, starting with young seedlings planted singly at wider spacing in a square pattern; and with intermittent irrigation that keeps the soil moist but not inundated, and frequent inter cultivation with weeder that actively aerates the soil.
Horticulture and Vegetable
This involves the cultivation of vegetables and horticulture in a measured model by intercropping different crops together. The model ensures proper growth of the plants pest management and crop rotation depending on the season, providing a year-round food supply and income to the farmer
Pig Rearing
Piggery is a major source of livelihood in the rural northeast. However traditional rearing practices has not been profitable in the last few as rearing in the open is prone to different illness and disease-causing organism leading to loss of weight and mortality. SeSTA therefore supports these farmers with advanced scientific method of rearing pigs to reduce mortality ensuring productivity and maximum profit
Goat Rearing
As goat is widely reared in the rural northeast. A proper goat rearing model is introduced with poor and socially disadvantaged households. The model is aimed at providing support to small/ marginal farmers and landless laborers who suffers due to variety of reasons including limited access to common lands and free grazing areas, lack of housing facilities and low investment capacities.
Nutrition-Garden
SeSTA capitalizes on the garden promotes a Nutrition-garden model for improving nutritional outcomes, which will ensure dietary diversity and boost the immunity of the consumers.
The garden is designed to support intercropping in the SCI method of cultivation and immediate replacement with new crops according to the seasonal crop calendar of the particular geography thereby sustaining the nutrition diversity and also enhancing the income by selling the surplus production
Farm Pond
The farm pond is introduced to promote fish culture and the water in it will act as a substitute during the dry seasons to other crops and paddy cultivation. The model is designed for 1 bigha of pond, which will host at least five different species of fish (Rahu, Common Carp, Grass Crap, Mrigal and Katla). The bandhs of the pond will also host vegetables and other orchard plants like banana.
